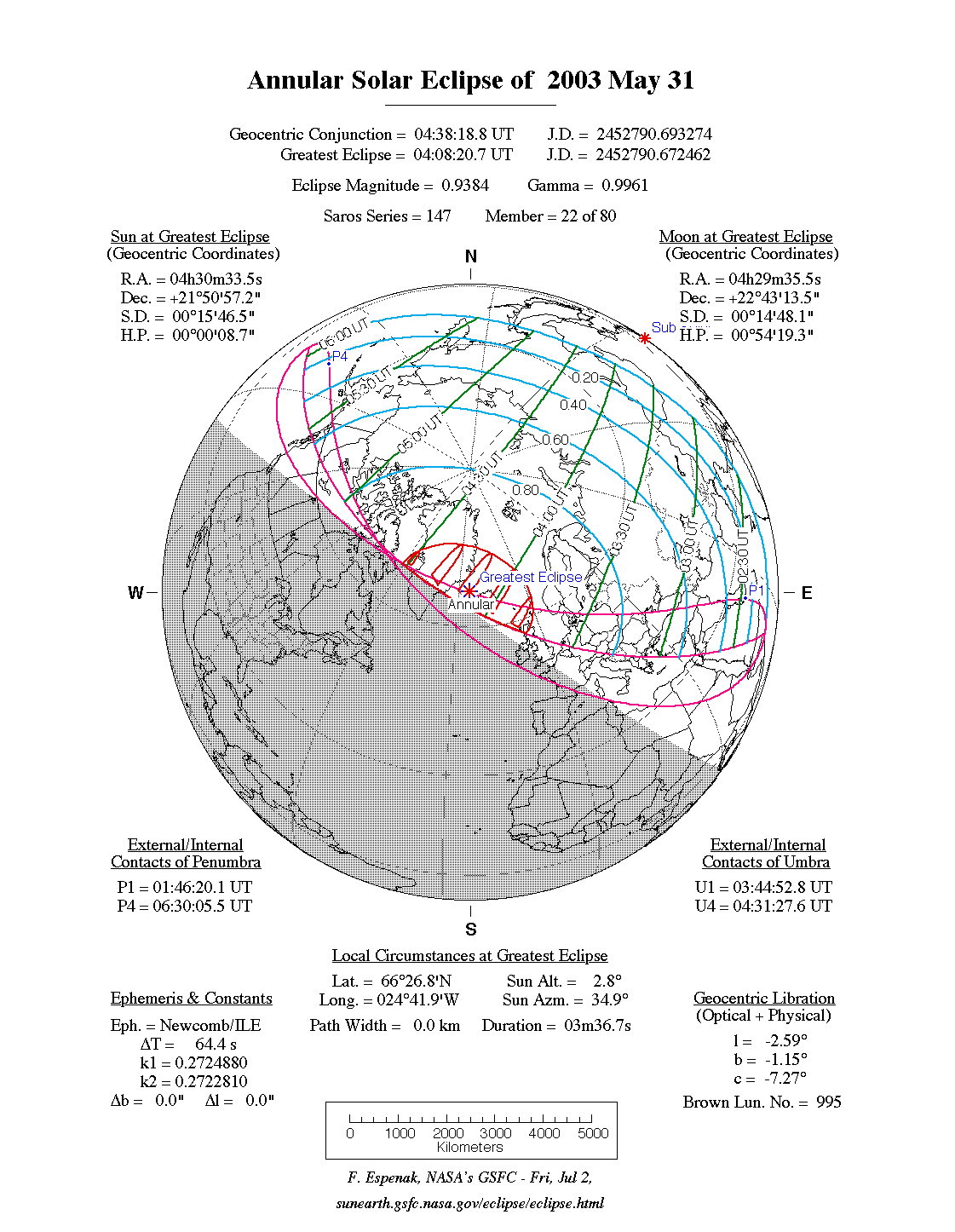
An annular eclipse of the Sun occurred on Saturday 31 May, 2003 UT, lasting from 01:46–06:30 UT. This was a marginal annular eclipse, lasting 3 minutes and 37 seconds, with the annular path visible in far north-west Scotland, Iceland, and Greenland. The partial eclipse was visible from much of northern Asia and Europe.
The timings of the phases of the overall eclipse
worldwide are as follows. In any particular
place it would have been seen for a significantly shorter
duration as the shadow moved across the Earth:
| Partial eclipse began: |
01:46:20 UT |
| Annular eclipse began: |
03:44:53 UT |
| Maximum eclipse: |
04:08:21 UT |
| Annular eclipse ended: |
04:31:28 UT |
| Partial eclipse ended: |
06:30:05 UT |
During this eclipse the Sun was 0.526° in apparent
diameter, 1.3% smaller than average. The Moon was just 2 days past apogee, making it extremely small.
At maximum eclipse it was 0.494° in
apparent diameter, which is 7.0% smaller than average; this was not
large enough to cover the Sun, which is why this
was an annular eclipse.
The statistics page has information on the ranges of the sizes of
the Sun and Moon, and the Moon data page displays detailed
information on the Moon's key dates.
The next eclipse in the triple-Saros series will happen on Jul 1, 2057, but will not be visible in Britain. However, two eclipses later in the same Saros series, an eclipse is visible in central Britain on Jul 23 2093.
An annular eclipse — the first central (ie. not partial) eclipse in its series — covers the top of the Earth, and partly misses it entirely. Large parts of Greenland will see the eclipse, and the centre line passes over Iceland. For the UK, it will be seen in most of the Highlands, including Inverness, the Orkneys, Shetlands, and Lewis, at around dawn. The rest of the UK will see the Sun rise partially eclipsed.
Interactive Map
This map shows the visibility of the eclipse.
The shaded area saw the annular solar eclipse; however, near the edges of
this area, the eclipse was very short. The bold line shows the centre
of the path, where the eclipse lasted longest.
Use the zoom controls to zoom in and out; hover your mouse over any
point on the centreline to see the time and
duration of the eclipse at that point. You can pan and zoom the map to
see detail for any part of the eclipse path.
The interactive map is currently not available.
Overview Map
This map sourced from NASA Goddard Space flight Center: GSFC Eclipse Web SiteGSFC Eclipse Web Site
The primary source of all the information on eclipses presented here at Hermit Eclipse. (NASA Goddard Space flight Center)
shows the visibility of the annular solar eclipse. It also shows the broader area in which a partial eclipse was seen. (Click on it for the
full-sized version.)
Eclipse Season and Saros Series
This eclipse season contains 2 eclipses:
This was the 22nd eclipse in solar Saros series 147.The surrounding eclipses in this Saros series are:
This Saros series, solar Saros series 147,
is linked to lunar Saros series 140. The
nearest partner eclipses in that series are:
Eclipse Parameters
| UT Date/time (max) | 04:08:18 on 31 May UT |
TDT Date/time (max) | 04:09:22 on 31 May TDT |
| Saros Series | 147 |
Number in Series | 22 |
| Penumbral Magnitiude | |
Central Magnitiude | 0.9384 |
| Gamma | 0.996 |
Path Width (km) | 0 |
| Delta T | 1m04s |
Error | ± 0m00s (95%) |
| Penumbral Duration | |
Partial Duration | |
| Total Duration | 3m37s |
| |
| Partial Rating | |
Total Rating | |
| Sun Distance | 151670899 km (94.6%) |
Moon Distance | 403660 km (94.0%) |
| Sun Diameter | 0.526° |
Moon Diameter | 0.493° - 0.494° |
| Apogee | 13:05 on 28 May UT |
Perigee | 23:19 on 12 Jun UT |
| Contact p1 | 01:46:20 on 31 May UT |
Contact p2 | |
| Contact u1 | 03:44:53 on 31 May UT |
Contact u2 | |
| Max eclipse | 04:08:21 on 31 May UT |
| Contact u3 | |
Contact u4 | 04:31:28 on 31 May UT |
| Contact p3 | |
Contact p4 | 06:30:05 on 31 May UT |
Note that while all dates and times on this site (except
where noted) are in UT, which is within a second of civil time,
the dates and times shown in NASA's eclipse listingsGSFC Eclipse Web Site
The primary source of all the information on eclipses presented here at Hermit Eclipse. (NASA Goddard Space flight Center)
are in the TDT timescale.
The Sun and Moon distances are shown in km, and as a
percentage of their minimum - maximum distances; hence 0%
is the closest possible (Earth's perihelion, or the
Moon's closest possible perigee) and 100% is
the farthest (aphelion, the farthest apogee).
The statistics page has information on the ranges of sizes
of the Sun and Moon, and the Moon data page displays detailed
information on the Moon's key dates.
Data last updated: 2015-06-21 22:11:46 UTC.