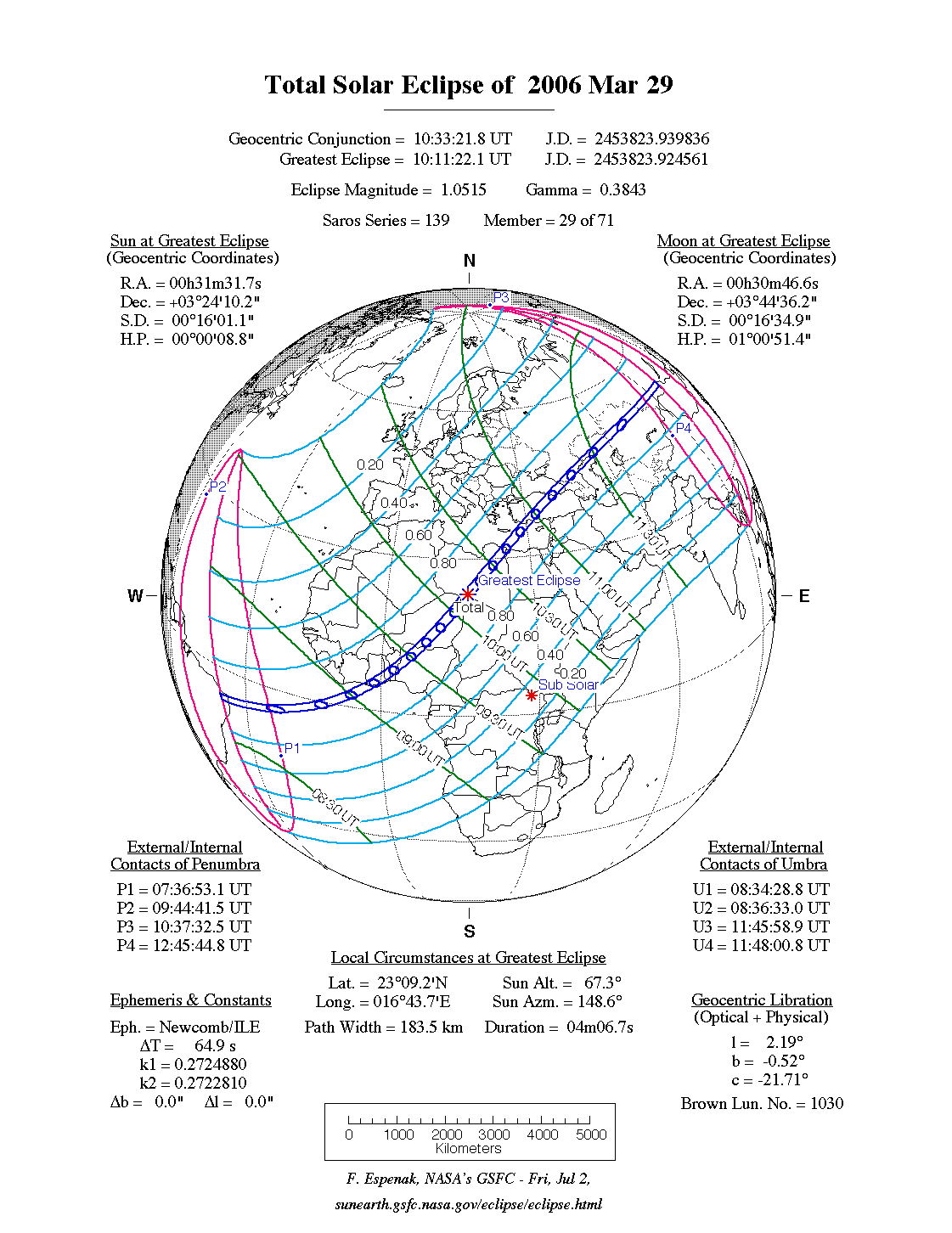
A total eclipse of the Sun occurred on Wednesday 29 March, 2006 UT, lasting from 07:36–12:45 UT. A dramatic total eclipse plunged the Sun into darkness for 4 minutes and 7 seconds at maximum, creating an amazing spectacle for observers in a broad path up to 184 km wide. It was seen from eastern Brazil, western Africa, across the eastern Med, and north-east through Asia. The partial eclipse was visible throughout Europe, though not spectacularly in Britain.
The timings of the phases of the overall eclipse
worldwide are as follows. In any particular
place it would have been seen for a significantly shorter
duration as the shadow moved across the Earth:
| Partial eclipse began: |
07:36:53 UT |
| Total eclipse began: |
08:34:29 UT |
| Maximum eclipse: |
10:11:22 UT |
| Total eclipse ended: |
11:48:01 UT |
| Partial eclipse ended: |
12:45:45 UT |
During this eclipse the Sun was 0.534° in apparent
diameter, around average. The Moon was just a day past perigee, making it very large.
At the start and end of the eclipse the Moon
was 0.552°, and at maximum eclipse 0.561°,
which is 5.7% larger than average; hence it covered the Sun,
making this a total eclipse.
The statistics page has information on the ranges of the sizes of
the Sun and Moon, and the Moon data page displays detailed
information on the Moon's key dates.
A major eclipse, and the last reasonably easy chance for Europeans to see a total eclipse of the Sun for many years, this will be a very significant event.
The total eclipse begins in the extreme east of Brazil, then crosses the Atlantic, passing through Ghana, Togo, Benin, Nigeria, Niger, Chad, Libya, and north-western Egypt on its way to the Med. It then crosses Turkey, Georgia, southern Russia, Kazakhstan, and Russia again, before finishing right on the Mongolian border.
Interactive Map
This map shows the visibility of the eclipse.
The shaded area saw the total solar eclipse; however, near the edges of
this area, the eclipse was very short. The bold line shows the centre
of the path, where the eclipse lasted longest.
Use the zoom controls to zoom in and out; hover your mouse over any
point on the centreline to see the time and
duration of the eclipse at that point. You can pan and zoom the map to
see detail for any part of the eclipse path.
The interactive map is currently not available.
Overview Map
This map sourced from NASA Goddard Space flight Center: GSFC Eclipse Web SiteGSFC Eclipse Web Site
The primary source of all the information on eclipses presented here at Hermit Eclipse. (NASA Goddard Space flight Center)
shows the visibility of the total solar eclipse. It also shows the broader area in which a partial eclipse was seen. (Click on it for the
full-sized version.)
Eclipse Season and Saros Series
This eclipse season contains 2 eclipses:
This was the 29th eclipse in solar Saros series 139.The surrounding eclipses in this Saros series are:
This Saros series, solar Saros series 139,
is linked to lunar Saros series 132. The
nearest partner eclipses in that series are:
Eclipse Parameters
| UT Date/time (max) | 10:11:18 on 29 Mar UT |
TDT Date/time (max) | 10:12:23 on 29 Mar TDT |
| Saros Series | 139 |
Number in Series | 29 |
| Penumbral Magnitiude | |
Central Magnitiude | 1.0515 |
| Gamma | 0.3843 |
Path Width (km) | 184 |
| Delta T | 1m05s |
Error | ± 0m00s (95%) |
| Penumbral Duration | |
Partial Duration | |
| Total Duration | 4m07s |
| |
| Partial Rating | |
Total Rating | |
| Sun Distance | 149366296 km (47.0%) |
Moon Distance | 360318 km (7.8%) |
| Sun Diameter | 0.534° |
Moon Diameter | 0.552° - 0.561° |
| Perigee | 07:13 on 28 Mar UT |
Apogee | 13:17 on 9 Apr UT |
| Contact p1 | 07:36:53 on 29 Mar UT |
Contact p2 | |
| Contact u1 | 08:34:29 on 29 Mar UT |
Contact u2 | 08:36:33 on 29 Mar UT |
| Max eclipse | 10:11:22 on 29 Mar UT |
| Contact u3 | 11:45:59 on 29 Mar UT |
Contact u4 | 11:48:01 on 29 Mar UT |
| Contact p3 | |
Contact p4 | 12:45:45 on 29 Mar UT |
Note that while all dates and times on this site (except
where noted) are in UT, which is within a second of civil time,
the dates and times shown in NASA's eclipse listingsGSFC Eclipse Web Site
The primary source of all the information on eclipses presented here at Hermit Eclipse. (NASA Goddard Space flight Center)
are in the TDT timescale.
The Sun and Moon distances are shown in km, and as a
percentage of their minimum - maximum distances; hence 0%
is the closest possible (Earth's perihelion, or the
Moon's closest possible perigee) and 100% is
the farthest (aphelion, the farthest apogee).
The statistics page has information on the ranges of sizes
of the Sun and Moon, and the Moon data page displays detailed
information on the Moon's key dates.
Data last updated: 2015-06-21 22:11:46 UTC.