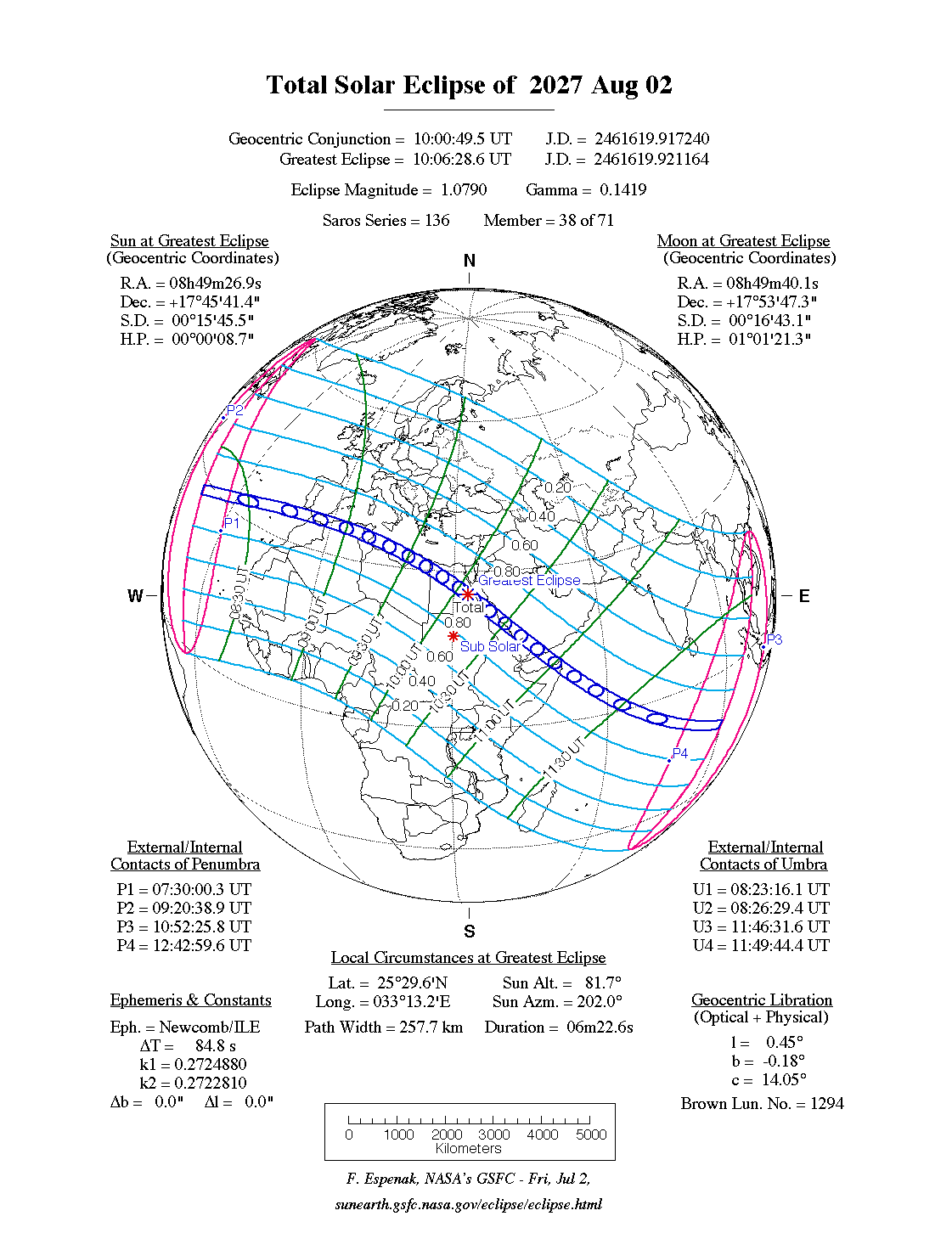
A total eclipse of the Sun occurs on Monday 2 August, 2027 UT, lasting from 07:30–12:43 UT. A dramatic total eclipse will plunge the Sun into darkness for 6 minutes and 23 seconds at maximum, creating an amazing spectacle for observers in a very broad path, 258 km wide at maximum. It will be seen across the southern tip of Spain, Gibraltar, and North Africa, and the Middle East. The partial eclipse will be visible across most of Africa, Europe, and south Asia.
The timings of the phases of the overall eclipse
worldwide are as follows. In any particular
place it will be seen for a significantly shorter
duration as the shadow moves across the Earth:
| Partial eclipse begins: |
07:30:00 UT |
| Total eclipse begins: |
08:23:16 UT |
| Maximum eclipse: |
10:06:29 UT |
| Total eclipse ends: |
11:49:44 UT |
| Partial eclipse ends: |
12:43:00 UT |
During this eclipse the Sun will be 0.525° in apparent
diameter, 1.4% smaller than average. The Moon will be at perigee, making it extremely large.
At the start and end of the eclipse the Moon
will be 0.557°, and at maximum eclipse 0.567°,
which is 6.7% larger than average; hence it will cover the Sun,
making this a total eclipse.
The statistics page has information on the ranges of the sizes of
the Sun and Moon, and the Moon data page displays detailed
information on the Moon's key dates.
Europe and West Africa
The eclipse starts in the Atlantic, passes north of Funchal, and makes landfall around the Strait of Gibraltar at about 08:46 UT. The centreline actually crosses south of Tangier, which will see a spectacular total eclipse lasting well over 4 minutes; but viewers in southern Spain and Gibraltar will also see a superb and long-lasting total eclipse.
From there, the centreline of the eclipse crosses the sea to Oran, which it reaches at about 08:53 UT; but people on the African coast in between will still see a very cool total eclipse. From Oran, the path of totality bends south, missing Algiers, but giving the many people in the path an amazing spectacle of a total eclipse lasting over 5 minutes. The path reaches the sea at Sfax at around 09:12 UT, where the eclipse path will be 248 km (154.1 miles) wide, and the eclipse will last 5 minutes and 40 seconds for viewers on the centreline.
East Africa, Middle East
The path of totality just clips the coast at Tajoura, but so close to the edge the eclipse will be very short-lived; so this will be a very poor vntage point. At 09:30 UT the eclipse makes landfall fully at Benghazi, where the total eclipse wil last over 6 minutes on the centreline, with a path 253 km (157.2 miles) wide. It then crosses into Egypt at 09:42 UT, and passes over Luxor at 10:05 UT; at just a minute before maximum eclipse, the duration of the total eclipse is now approaching 6 and a half minutes.
The centreline reaches the Red Sea at 10:14 UT, at the Elba National Park; the same area will see a total solar eclipse in March 2034. The eclipse path then crosses to Jeddah and Mecca, which it will pass at around 10:26 UT. Although both cities will see a total eclipse, the longest duration will be seen on the coast south of Jeddah, where a total eclipse lasting over 6 minutes will be seen.
The centreline of the eclipse runs down the coast, and then crosses into Yemen at 10:40 UT. Unfortunately the path of the eclipse just grazes Sana'a; although it will see a short total eclipse, a much better viewpoint would be around 120 km (74.6 miles) to the north-east, where the eclipse will last close to 6 minutes.
The eclipse reaches the Gulf of Aden at 10:53 UT, then hits Somalia at 11:00 UT. The eclipse will be best seen in Qandala, or slightly east; although it is drawing to a close at this point, it will still last 5 and a half minutes on the centreline.
Finally the eclipse passes into the Indian Ocean at 11:04 UT; it will pass over some of the atolls of the Chagos Archipelago at about 11:41 UT, then finishes in the ocean at 11:49 UT.
Interactive Map
This map shows the visibility of the eclipse.
The shaded area will see the total solar eclipse; however, near the edges of
this area, the eclipse will be very short. The bold line shows the centre
of the path, where the eclipse will last longest, so this is where you want to be if possible.
Use the zoom controls to zoom in and out; hover your mouse over any
point on the centreline to see the time and
duration of the eclipse at that point. You can pan and zoom the map to
see detail for any part of the eclipse path.
The interactive map is currently not available.
Overview Map
This map sourced from NASA Goddard Space flight Center: GSFC Eclipse Web SiteGSFC Eclipse Web Site
The primary source of all the information on eclipses presented here at Hermit Eclipse. (NASA Goddard Space flight Center)
shows the visibility of the total solar eclipse. It also shows the broader area in which a partial eclipse will be seen. (Click on it for the
full-sized version.)
Eclipse Season and Saros Series
This eclipse season contains 3 eclipses:
This is the 38th eclipse in solar Saros series 136.The surrounding eclipses in this Saros series are:
This Saros series, solar Saros series 136,
is linked to lunar Saros series 129. The
nearest partner eclipses in that series are:
Eclipse Parameters
| UT Date/time (max) | 10:06:34 on 2 Aug UT |
TDT Date/time (max) | 10:07:50 on 2 Aug TDT |
| Saros Series | 136 |
Number in Series | 38 |
| Penumbral Magnitiude | |
Central Magnitiude | 1.079 |
| Gamma | 0.1421 |
Path Width (km) | 258 |
| Delta T | 1m16s |
Error | ± 0m10s (95%) |
| Penumbral Duration | |
Partial Duration | |
| Total Duration | 6m23s |
| |
| Partial Rating | major |
Total Rating | major |
| Sun Distance | 151828567 km (97.9%) |
Moon Distance | 357387 km (2.0%) |
| Sun Diameter | 0.525° |
Moon Diameter | 0.557° - 0.567° |
| Perigee | 06:28 on 2 Aug UT |
Apogee | 14:24 on 15 Aug UT |
| Contact p1 | 07:30:00 on 2 Aug UT |
Contact p2 | |
| Contact u1 | 08:23:16 on 2 Aug UT |
Contact u2 | 08:26:29 on 2 Aug UT |
| Max eclipse | 10:06:29 on 2 Aug UT |
| Contact u3 | 11:46:32 on 2 Aug UT |
Contact u4 | 11:49:44 on 2 Aug UT |
| Contact p3 | |
Contact p4 | 12:43:00 on 2 Aug UT |
Note that while all dates and times on this site (except
where noted) are in UT, which is within a second of civil time,
the dates and times shown in NASA's eclipse listingsGSFC Eclipse Web Site
The primary source of all the information on eclipses presented here at Hermit Eclipse. (NASA Goddard Space flight Center)
are in the TDT timescale.
The Sun and Moon distances are shown in km, and as a
percentage of their minimum - maximum distances; hence 0%
is the closest possible (Earth's perihelion, or the
Moon's closest possible perigee) and 100% is
the farthest (aphelion, the farthest apogee).
The statistics page has information on the ranges of sizes
of the Sun and Moon, and the Moon data page displays detailed
information on the Moon's key dates.
Data last updated: 2015-09-17 04:54:30 UTC.